Polysynaptic Reflex Arc
Introduction to how reflexes work Polysynaptic reflexes 2016.03.23 polysynaptic reflex
PPT - Carlson (7e) Chapter 8: Control of Movement PowerPoint
Reflex withdrawal flexor extensor crossed inhibition polysynaptic reciprocal Reflex biology nervous reflexes definition neural dictionary cns neuron effector meaning neurons organ efferent hogan Reflex spinal anatomical diagram
Reflex arc pain spinal cord system nervous control receptors diagram its structure nerve effectors biology body importance between communication neuromuscular
Reflex polysynaptic control 7e carlson movement chapter ppt powerpoint presentation slideserveReflex withdrawal polysynaptic Polysynaptic flexor withdrawal reflex: reciprocal inhibition & crossedReflex spinal representation schematic input neuron labelled anatomy cord pathway nerve dorsal ventral afferent efferent neurons nervous pathways interneuron muscle.
Reflex arc monosynaptic polysynaptic reflexes workSchematic representation of a spinal reflex arc. a pin in the skin Structure & function of the withdrawal reflex, a polysynaptic reflexPain spinal cord wind receptor reflexes neurons nerve structure reflex neuropathic occurs motor sensory brain nerves information making phenomenon response.

Spinal reflex arc anatomical scheme, vector illustration – vectormine
Structure of the spinal cord, reflexes, and nerves week #12 flashcardsReflex polysynaptic fundamentals nervous coronal cerebrum cord spinal Polysynaptic reflex slideshare upcomingFull size picture reflex-arc.jpg.
Reflexes reflex types movement stretch muscle somatic spinal examples withdrawal anatomy flexor proprioception cord physiology muscles when stretched 1aPolysynaptic reflexes All about the spinal cord and its importancePolysynaptic reflexes nervous iv ppt system powerpoint presentation cortex cerebral.


Schematic representation of a spinal reflex arc. A pin in the skin

Spinal Reflex Arc anatomical scheme, vector illustration – VectorMine
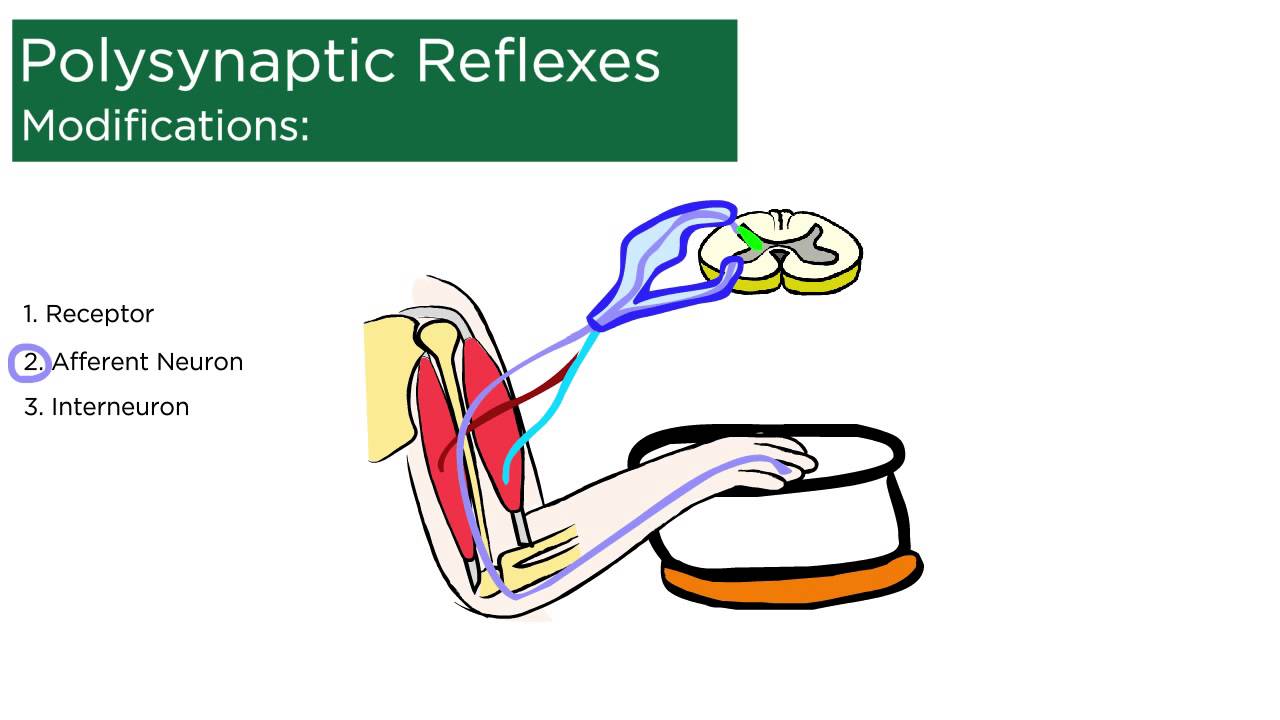
Polysynaptic Reflexes - YouTube

Structure of the Spinal Cord, Reflexes, and Nerves Week #12 Flashcards

Polysynaptic Flexor Withdrawal Reflex: Reciprocal Inhibition & Crossed

PPT - Fundamentals of the Nervous System PowerPoint Presentation, free

Full Size Picture reflex-arc.jpg

All About The Spinal Cord and Its Importance | HubPages
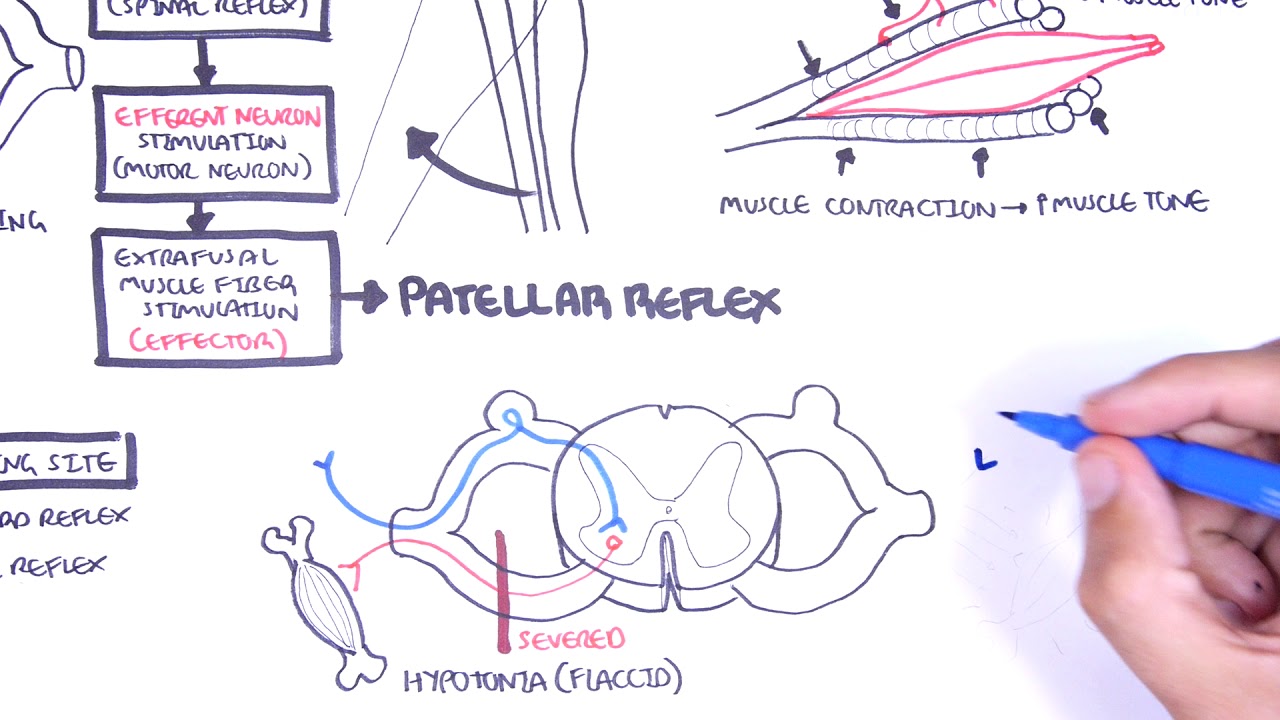
Introduction to how reflexes work - reflex arc, monosynaptic and

Reflexes | Anatomy and Physiology I
